In a recent study, researchers recruited schoolchildren, ages 9 and 10, who lived near the Champaign-Urbana campus of the University of Illinois and asked them to run on a treadmill. The researchers were hoping to learn more about how fitness affects the immature human brain. Animal studies had already established that, when given access to running wheels, baby rodents bulked up their brains, enlarging certain areas and subsequently outperforming sedentary pups on rodent intelligence tests. But studies of the effect of exercise on the actual shape and function of children’s brains had not yet been tried.
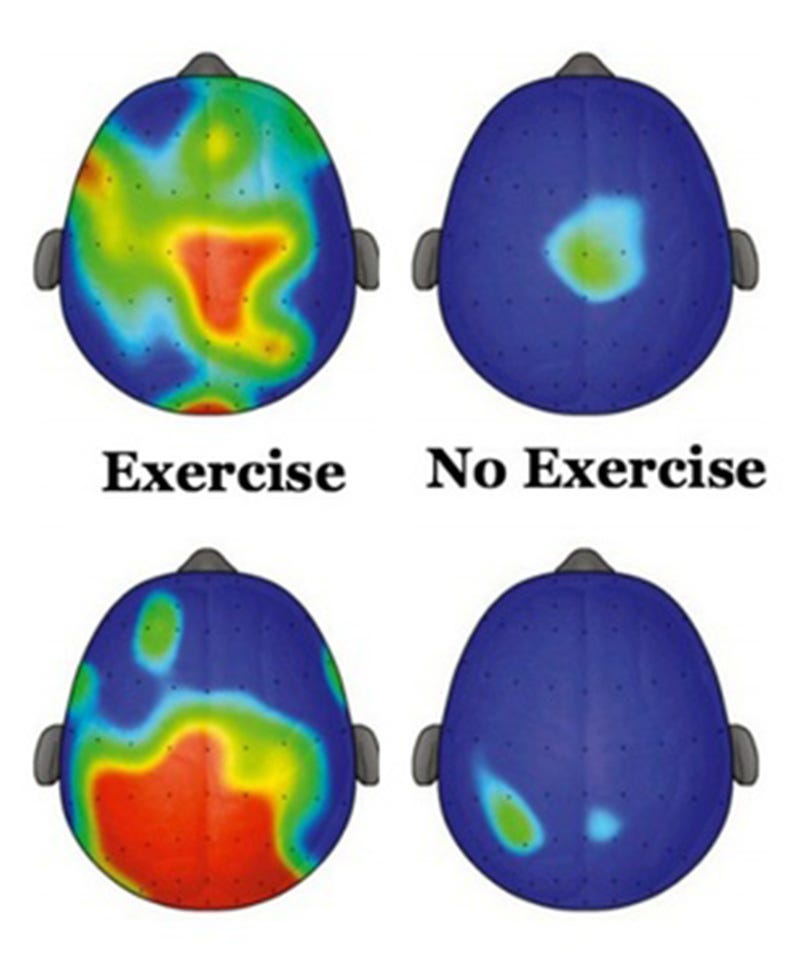
So the researchers sorted the children, based on their treadmill runs, into highest-, lowest- and median-fit categories. Only the most- and least-fit groups continued in the study (to provide the greatest contrast). Both groups completed a series of cognitive challenges involving watching directional arrows on a computer screen and pushing certain keys in order to test how well the children filter out unnecessary information and attend to relevant cues. Finally, the children’s brains were scanned, using magnetic resonance imaging technology to measure the volume of specific areas.
Previous studies found that fitter kids generally scored better on such tests. And in this case, too, those children performed better on the tests. But the M.R.I.’s provided a clearer picture of how it might work. They showed that fit children had significantly larger basal ganglia, a key part of the brain that aids in maintaining attention and “executive control,” or the ability to coordinate actions and thoughts crisply. Since both groups of children had similar socioeconomic backgrounds, body mass index and other variables, the researchers concluded that being fit had enlarged that portion of their brains.
Meanwhile, in a separate, newly completed study by many of the same researchers at the University of Illinois, a second group of 9- and 10-year-old children were also categorized by fitness levels and had their brains scanned, but they completed different tests, this time focusing on complex memory. Such thinking is associated with activity in the hippocampus, a structure in the brain’s medial temporal lobes. Sure enough, the M.R.I. scans revealed that the fittest children had heftier hippocampi.
The two studies did not directly overlap, but the researchers, in their separate reports, noted that the hippocampus and basal ganglia regions interact in the human brain, structurally and functionally. Together they allow some of the most intricate thinking. If exercise is responsible for increasing the size of these regions and strengthening the connection between them, being fit may “enhance neurocognition” in young people, the authors concluded.
These findings arrive at an important time. For budgetary and administrative reasons, school boards are curtailing physical education, while on their own, children grow increasingly sluggish. Recent statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that roughly a quarter of children participate in zero physical activity outside of school.
At the same time, evidence accumulates about the positive impact of even small amounts of aerobic activity. Past studies from the University of Illinois found that “just 20 minutes of walking” before a test raised children’s scores, even if the children were otherwise unfit or overweight, says Charles Hillman, a professor of kinesiology at the university and the senior author of many of the recent studies.
But it’s the neurological impact of sustained aerobic fitness in young people that is especially compelling. A memorable years-long Swedish study published last year found that, among more than a million 18-year-old boys who joined the army, better fitness was correlated with higher I.Q.’s, even among identical twins. The fitter the twin, the higher his I.Q. The fittest of them were also more likely to go on to lucrative careers than the least fit, rendering them less likely, you would hope, to live in their parents’ basements. No correlation was found between muscular strength and I.Q. scores. There’s no evidence that exercise leads to a higher I.Q., but the researchers suspect that aerobic exercise, not strength training, produces specific growth factors and proteins that stimulate the brain, said Georg Kuhn, a professor at the University of Gothenburg and the senior author of the study.
But for now, the takeaway is clear. “More aerobic exercise” for young people, Mr. Kuhn said. Mr. Hillman agreed. So get kids moving, he added, and preferably away from their Wiis. A still-unpublished study from his lab compared the cognitive impact in young people of 20 minutes of running on a treadmill with 20 minutes of playing sports-style video games at a similar intensity. Running improved test scores immediately afterward. Playing video games did not.
This is the abstract of the original study and link to read it.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3696376/
Abstract
The present investigation is the first to explore the association between childhood aerobic fitness and basal ganglia structure and function. Rodent research has revealed that exercise influences the striatum by increasing dopamine signaling and angiogenesis. In children, higher aerobic fitness levels are associated with greater hippocampal volumes, superior performance on tasks of attentional and interference control, and elevated event-related brain potential indices of executive function. The present study used magnetic resonance imaging to investigate if higher-fit and lower-fit 9- and 10-year-old children exhibited differential volumes of other subcortical brain regions, specifically the basal ganglia involved in attentional control. The relationship between aerobic fitness, dorsal and ventral striatum volumes and performance on an attention and inhibition Eriksen flanker task was also examined. The results indicated that higher-fit children showed superior flanker task performance compared to lower-fit children. Higher-fit children also showed greater volumes of the dorsal striatum, and dorsal striatum volume was negatively associated with behavioral interference. The results support the claim that the dorsal striatum is involved in cognitive control and response resolution and that these cognitive processes vary as a function of aerobic fitness. No relationship was found between aerobic fitness, the volume of the ventral striatum and flanker performance. The findings suggest that increased childhood aerobic fitness is associated with greater dorsal striatal volumes and that this is related to enhanced cognitive control. Because children are becoming increasingly overweight, unhealthy and unfit, understanding the neurocognitive benefits of an active lifestyle during childhood has important public health and educational implications.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.

No responses yet